1. Fact: You Can Improve Your Child's Immunity Before Birth
An expecting mother's health and immunity have a direct impact on the health and immunity of her developing baby. To support their immune health, moms should prioritize taking good care of themselves, including a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, exercise, stress reduction and plenty of sleep.
2. Fiction: The Gut Is Separate from the Immune System
Approximately 70 percent of the immune system is in our GI tract, where there are trillions of microscopic organisms. The balance of good bacteria in the gut is an important component in the immunity of the entire body.
3. Fact: Skin-to-Skin Contact Helps Baby's Immunity
Also called "kangaroo care," skin-to-skin contact with mom and dad, especially in the first few days after your baby is born, helps to transfer diverse microbes to enhance newborn immunity.
4. Fact: Probiotics Pass from Mom to Baby in the Womb
Breast milk contains Probiotics that are passed to baby during breastfeeding. Probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt and kefir can help to strengthen mom's immune system to support the baby's as well.
5. Fact: Breastmilk Contains Specialized Nutrients to Bolster Baby's Immunity
Milk the mother produces immediately following delivery is called colostrum and contains immune-strengthening antibodies, to help protect the baby in the first months of life. All breast milk is also rich in human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs). HMOs are special prebiotics that help feed the good bacteria in your baby's gut to support GI health and the developing immune system. Abbott's Similac® with 2′-FL HMO was the United States' first infant formula to provide HMOs to formula-fed babies.
6. Fiction: Parents Should Minimize How Often Baby Leaves Home in the First Six Months of Life
While babies are more susceptible to serious infection in the first six months of life, they do not need to live in a bassinet bubble. However, during a global pandemic new parents and guardians should refer to CDC guidelines and recommendations to protect children. And as always ask visitors to wash their hands or use hand sanitizer before holding or playing with your infant or newborn.
7. Fact: Having Pets Are Beneficial to the Immune System
For most young children, new experiences and interactions are opportunities to build new antibodies and strengthen the immune system. Studies even show that safe interaction with pets can impact the composition and diversity of the microbes in a child's gut, and may help prevent the development of asthma
8. Fiction: Sleep is Not Important To Your Immune System
A solid night’s rest will do wonders for how you feel the next day. But getting the right amount of sleep can support your immune system and strengthen our body’s defenses.
9. Fact: By Age 3, a Child's Immune System Becomes Stable
The first year of life is a critical window for immune development — by about age three the system will be more mature. However, it's important to remember that, even after your child's third birthday, new foods, activities, illnesses and courses of antibiotics can affect the health of gut bacteria and the immune system.
10. Fact: Childhood Nutrition Can Nourish a Developing Immune System
Even after breastfeeding or formula feeding has stopped, nutrition and immunity are intricately linked. As your baby begins to eat solid food, offer whole foods and whole-food purees including fruits, vegetables and grains. They are rich in prebiotics, which help probiotics strengthen the infant immune system via the gut.
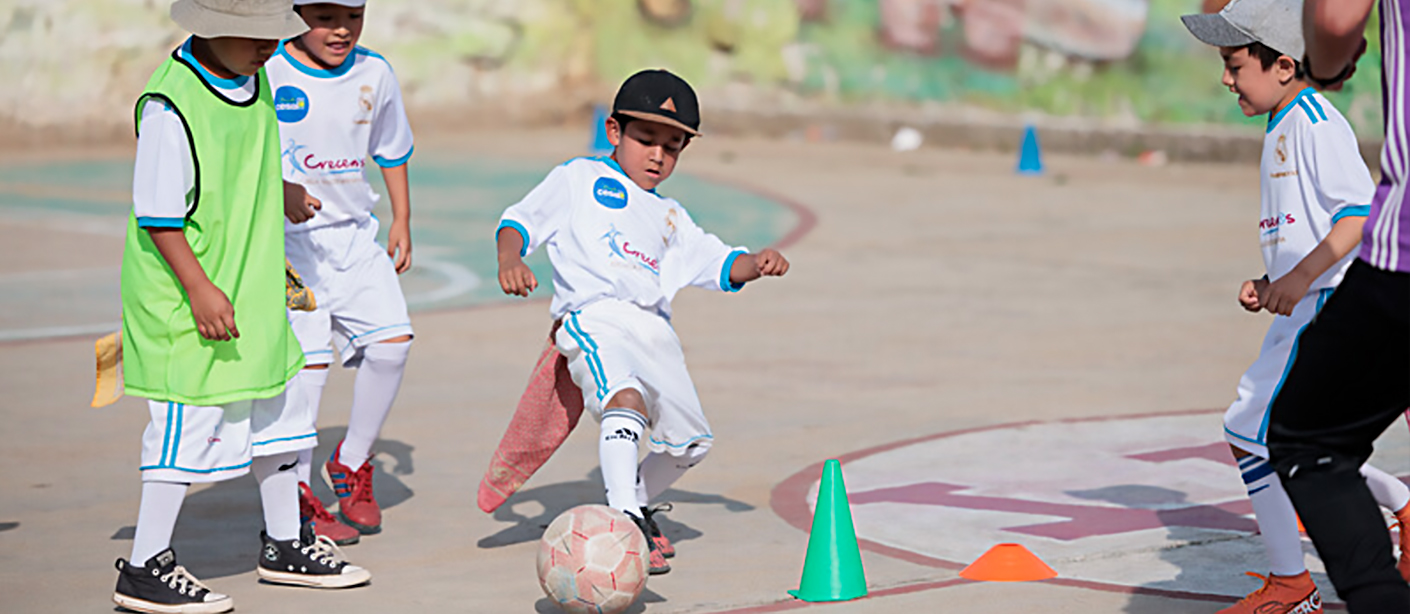
11. Fiction: Exercise Does Not Affect a Child's Growing Immunity
Research shows that exercise may also diversify your child's gut microbes to strengthen the immune system. Encourage active playtime with your child at home, in the backyard or at the park.
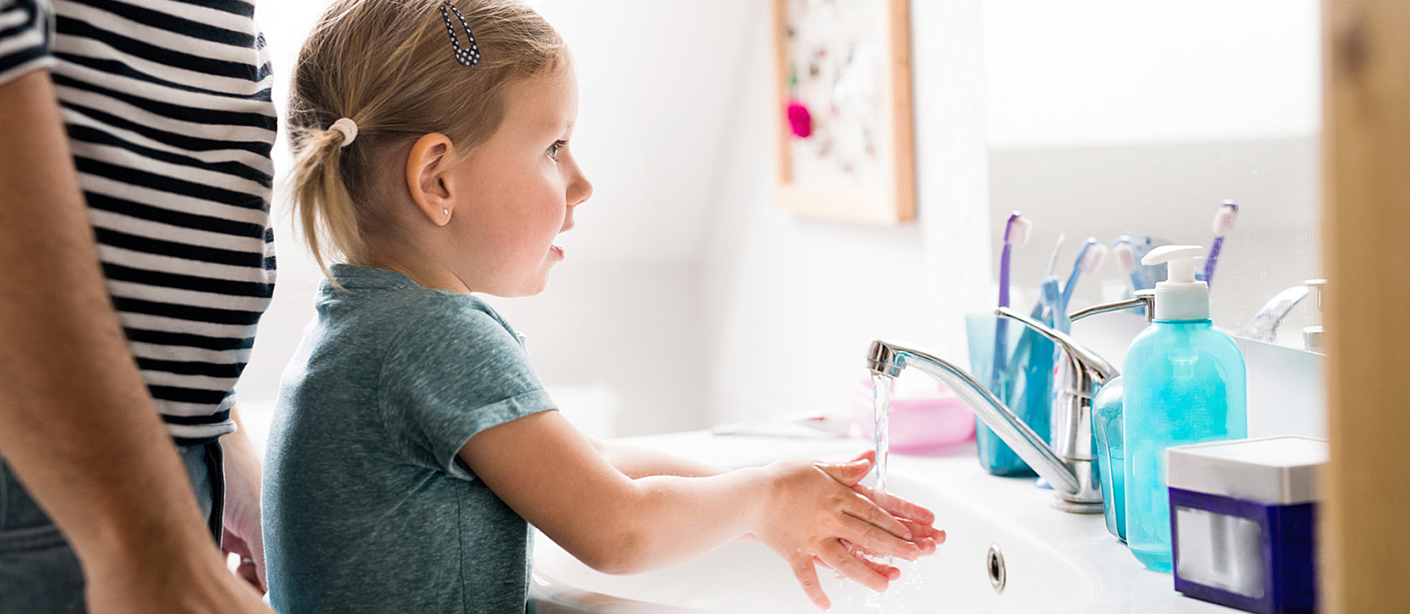
12. Fact: Washing Your Hands Can Prevent Illness
Regularly washing hands and teaching proper hygiene can help to prevent the spread of common illnesses. According to the CDC, handwashing with soap could protect about 1 out of every 3 young children who get sick with diarrhea and almost 1 out of 5 young children with respiratory infections like pneumonia.



Social Share