The Role of Protein in the Body, Other Nutrients at Different Ages
- Sub Heading
-
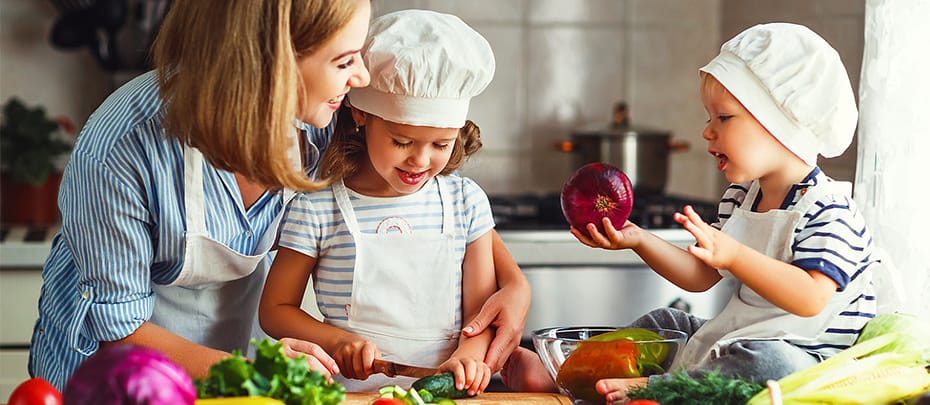
Important nutrients for each and every chapter of your life.
- Main Image
-

- Duration
-
MAR. 06, 2019 6 MIN. READ - Description
-
Just as your body changes with each stage of life, your nutrition needs change too. Consider the role of protein in the body. In infancy, it's a critical part of growth and development; while in adulthood, protein may help you maintain a healthy BMI or body mass index. And as you age, it can help you support the lean muscle you need to stay active.
The same holds true for other nutrients like vitamins, minerals and certain fats. Researchers at Abbott have been studying the role nutrition plays from early infancy to late adulthood to help people better nourish every stage of life. If you're wondering which nutrients you need now — and in the future — these experts share the latest insights from nutrition science.


Social Share