The Connection Between Muscles, the Immune System and Diabetes Management
Muscles are well-known for their role in movement, and muscle preservation is vital for maintaining strength and function as we age.2 There is evidence suggesting muscles play a role in immune function, as well. Muscles produce and release compounds which play an important role in the creation, activation, and distribution of some immune cells.3 Muscles are also key sources for amino acids used by the body during a trauma or infection.4
Low muscle mass and inadequate protein intake may weaken the body’s response to an injury or infection, and emerging research suggests loss of muscle mass is associated with compromised immunity and infections.5
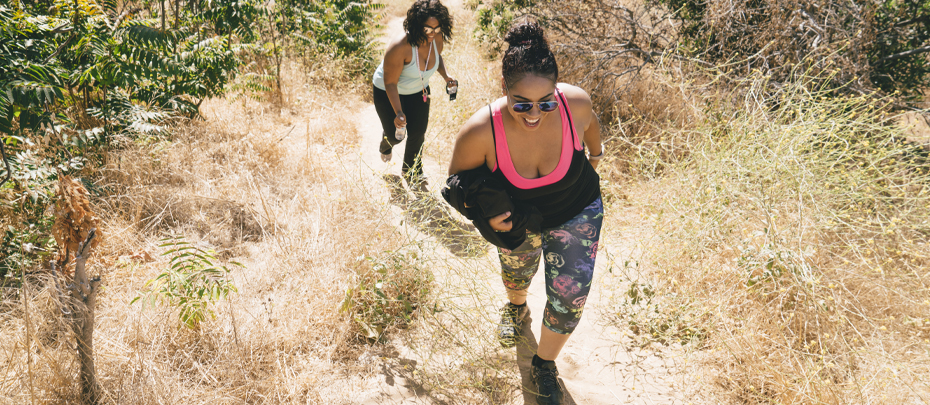
While it’s important for everyone to prioritize their muscle health and prevent muscle loss as they age, those living with diabetes need to be even more vigilant: diabetes accelerates muscle loss, reduces muscle quality, and diminishes strength.6
Healthy muscles help maintain body weight and insulin sensitivity, which is vital for maintaining blood sugar levels and keeping diabetes under control. There are steps that people with diabetes can take to maintain muscle and immune health, including staying physically active and eating a balanced diet.
Supporting Muscle Health and Immunity through a Healthy Lifestyle
Exercising regularly – aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise a week – and eating a well-rounded diet are essential to staying healthy, supporting muscles, and helping those with diabetes manage their blood sugar. Important steps to support your muscle and immune health through nutrition include:
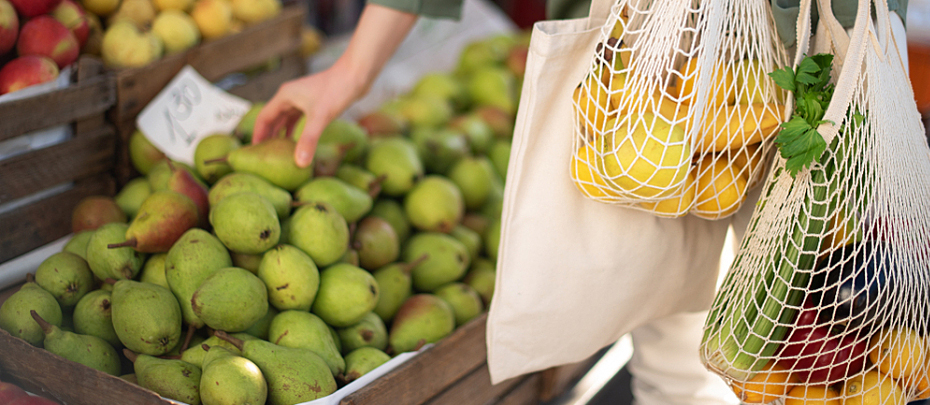
- Maintaining a balanced diet full of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, proteins, and healthy fats.
- Eating enough protein-rich foods like chicken, seafood, eggs, nuts, beans or dairy. Adults should aim to eat about 25-30 grams of protein per meal. However, adults over the age of 65 may need more protein than younger adults – particularly those with a health setback.7
- Prioritizing quality foods that contain nutrients to support a healthy immune system, such as vitamin C, zinc, vitamin E, vitamin A and vitamin D.
It’s not always easy to get enough of all the nutrients needed to adequately support muscle and immune health, especially for people with diabetes who also need to stay on top of their medications and routines and feel they don’t have enough time to plan ahead when it comes to meals and snacks. Studies have shown that diabetes-specific nutritional supplements – as part of a healthy lifestyle program – can help close that gap and provide the proper nutrients, resulting in improved health outcomes in people with diabetes. These include better glycemic control, improved blood pressure, reduced or maintained body weight and, in critically ill patients with diabetes, lower mortality.8,9,10,11



Social Share